








 Tegheya Kte
Tegheya Kte
WASHINGTON (AFP) — The Lakota Indians, who gave the world legendary warriors Sitting Bull and Crazy Horse, have withdrawn from treaties with the United States, leaders said Wednesday.
"We are no longer citizens of the United States of America and all those who live in the five-state area that encompasses our country are free to join us," long-time Indian rights activist Russell Means told a handful of reporters and a delegation from the Bolivian embassy, gathered in a church in a run-down neighborhood of Washington for a news conference.
A delegation of Lakota leaders delivered a message to the State Department on Monday, announcing they were unilaterally withdrawing from treaties they signed with the federal government of the United States, some of them more than 150 years old.
They also visited the Bolivian, Chilean, South African and Venezuelan embassies, and will continue on their diplomatic mission and take it overseas in the coming weeks and months, they told the news conference.
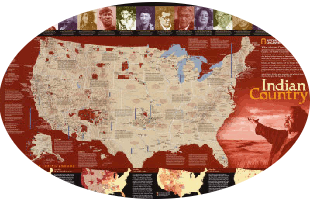
Lakota country includes parts of the states of Nebraska, South Dakota, North Dakota, Montana and Wyoming.
The new country would issue its own passports and driving licences, and living there would be tax-free -- provided residents renounce their US citizenship, Means said.
The treaties signed with the United States are merely "worthless words on worthless paper," the Lakota freedom activists say on their website.
The treaties have been "repeatedly violated in order to steal our culture, our land and our ability to maintain our way of life," the reborn freedom movement says.
Withdrawing from the treaties was entirely legal, Means said.
"This is according to the laws of the United States, specifically article six of the constitution," which states that treaties are the supreme law of the land, he said.
"It is also within the laws on treaties passed at the Vienna Convention and put into effect by the US and the rest of the international community in 1980. We are legally within our rights to be free and independent," said Means.
The Lakota relaunched their journey to freedom in 1974, when they drafted a declaration of continuing independence -- an overt play on the title of the United States' Declaration of Independence from England.
Thirty-three years have elapsed since then because "it takes critical mass to combat colonialism and we wanted to make sure that all our ducks were in a row," Means said.
One duck moved into place in September, when the United Nations adopted a non-binding declaration on the rights of indigenous peoples -- despite opposition from the United States, which said it clashed with its own laws.
"We have 33 treaties with the United States that they have not lived by. They continue to take our land, our water, our children," Phyllis Young, who helped organize the first international conference on indigenous rights in Geneva in 1977, told the news conference.
The US "annexation" of native American land has resulted in once proud tribes such as the Lakota becoming mere "facsimiles of white people," said Means.
Oppression at the hands of the US government has taken its toll on the Lakota, whose men have one of the shortest life expectancies -- less than 44 years -- in the world.
Lakota teen suicides are 150 percent above the norm for the United States; infant mortality is five times higher than the US average; and unemployment is rife, according to the Lakota freedom movement's website.
"Our people want to live, not just survive or crawl and be mascots," said Young.
"We are not trying to embarrass the United States. We are here to continue the struggle for our children and grandchildren," she said, predicting that the battle would not be won in her lifetime.
|
Sommaire de la rubrique
|
Haut de page
|